Инструкции
Подразделы

Вы когда-нибудь нажимали клавишу Shift слишком много
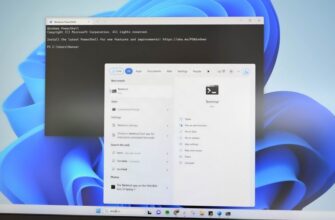
Инструменты командной строки могут показаться архаичным
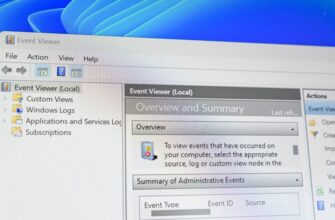
Процесс узла поставщика WMI является важной частью
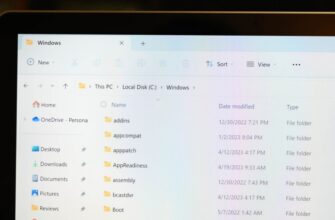
Предположим, вы ищете файл и знаете, что последний
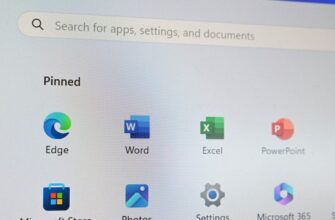
За прошедшие годы мы показали вам множество советов
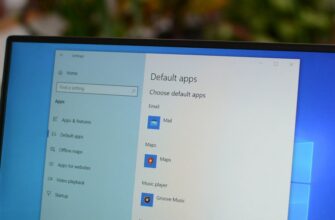
Microsoft Edge — это не только веб-браузер по умолчанию
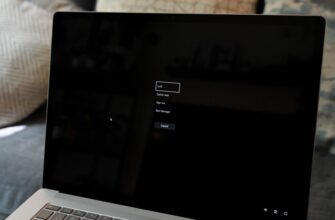
Один из наиболее распространенных шагов при устранении
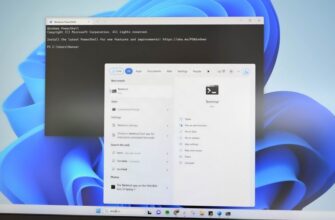
Изменить IP-адрес с помощью интерфейса панели управления
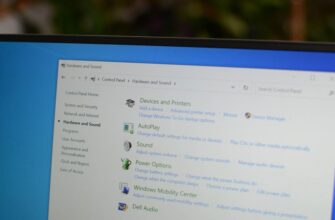
В наши дни большинство мобильных устройств оснащены

Согласно статистическим данным, WhatsApp используют

Изначально мессенджер WhatsApp разрабатывался как мобильное

Телеграмм – это популярный мессенджер для обмена текстовыми

При запуске мессенджера WhatsApp можно столкнуться

Как настроить микрофон в Дискорде? Такой вопрос обычно

По умолчанию, чтобы связаться с пользователем в мессенджере

Мессенджер WhatsApp задумывался для того, чтобы люди

Discord в настоящий момент является лучшей заменой

Черный экран при запуске Discord или же просто серый

Социальная сеть Одноклассники очень популярна среди

У социальной сети ВКонтакте есть официальное мобильное

Для входа в свой аккаунт ВКонтакте пользователю достаточно

Было бы очень неприятно потерять аккаунт ВКонтакте

Стикерами в социальной сети ВКонтакте называются стильные

В социальной сети ВК пользователи могут не только переписываться

Каждый пользователь ВКонтакте при регистрации указывает

В настоящий момент при регистрации профиля в социальной

В социальной сети ВКонтакте пользователи могут дарить
Подразделы

Загрузка другого веб-браузера — одна из первых задач

В Windows 10 изменить браузер по умолчанию очень просто

Google Chrome – достаточно быстрый браузер и очень

Пользователи подключают к компьютеру различные периферийные

Раньше пользователи могли пользоваться анонимной сетью

Chrome_elf.dll отсутствует что делать? Эта статья представляют

Web Graphics Library — это технология для браузеров.

Большинство веб-браузеров используют технологию WebRTC

В настоящий момент браузер Chrome от компании Google

Microsoft Teams — это один из наиболее широко используемых

В Google Meet есть множество функций, которые сделают

Microsoft Teams встроен в Windows 11 и доступен через

Если Microsoft Teams действует вам на нервы в Windows

Microsoft Teams — это один из наиболее широко используемых

Несмотря на то, что последние версии Windows хороши

Чтобы ваши виртуальные встречи проходили без сбоев

Если вы участвуете в групповом или индивидуальном чате
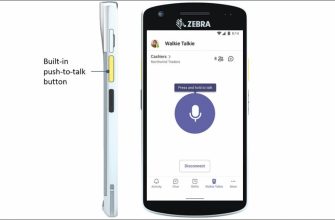
Microsoft представляет новый функция для Microsoft
![nod32-dlya-vindovs-hp-1[1]](https://sergoot.ru/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/nod32-dlya-vindovs-hp-11.png)
Пользователи Windows XP могут до сих пор использовать
![nod32-dlya-vindovs-7[1]](https://sergoot.ru/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/nod32-dlya-vindovs-71.png)
Рынок антивирусного ПО не стоит на месте.
![ESET-Remover[1]](https://sergoot.ru/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/ESET-Remover1.png)
Иногда продукты ESET невозможно удалить стандартным
![ESET-Live-Grid[1]](https://sergoot.ru/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/ESET-Live-Grid1.png)
ESET Live GRID – это утилита от словацкой компании
![Eset-Uninstaller[1]](https://sergoot.ru/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Eset-Uninstaller1.png)
Рано или поздно пользователям ПК приходится удалять
![NOD32[1]](https://sergoot.ru/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/NOD321.png)
Если вы устали от частых заражений компьютера различными
![Eset-Online-Scanner[1]](https://sergoot.ru/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Eset-Online-Scanner1.png)
При обнаружении вирусного заражения персонального компьютера
![NOD32[1]](https://sergoot.ru/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/NOD321.png)
ЕСЕТ Ремоут Администратор — это антивирусная среда
![Eset-Nod32-Mobile-Security-dlya-Android[1]](https://sergoot.ru/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Eset-Nod32-Mobile-Security-dlya-Android1.png)
С появлением интернета появилось очень много вредоносных

Все компьютеры оснащены графическим оборудованием

NVIDIA DLAA (сглаживание с глубоким обучением) — это

Блоки питания (БП) необходимы для работы компьютера.

Модули оперативной памяти — одна из самых важных частей
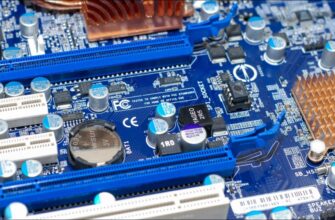
Чтобы проверить батарею CMOS, выключите блок питания

Основные различия между кэш-памятью L1, L2 и L3 заключаются

Нажмите Alt + Ctrl + Delete, чтобы открыть диспетчер задач.

Если вы осознаете и отвергнете все эти мифы и неправильные

Ожидается, что этап тестирования оперативной памяти
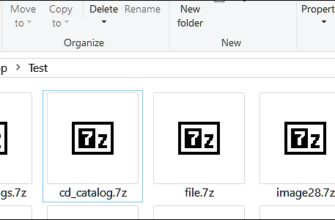
Вы почти наверняка когда-нибудь сталкивались с архивными
5G не представляет опасности для здоровья;

В современном мире гладких, необслуживаемых ноутбуков

Чтобы предотвратить проблемы с аккумулятором в игровом

SD-карта, изготовленная в соответствии со спецификацией

Ноутбуки из металла более долговечны и лучше рассеивают

Хороший USB-накопитель может работать 10 и более лет.

Объединение аудиофайлов по одному может занять много

Режим полета отключает все методы беспроводной связи
